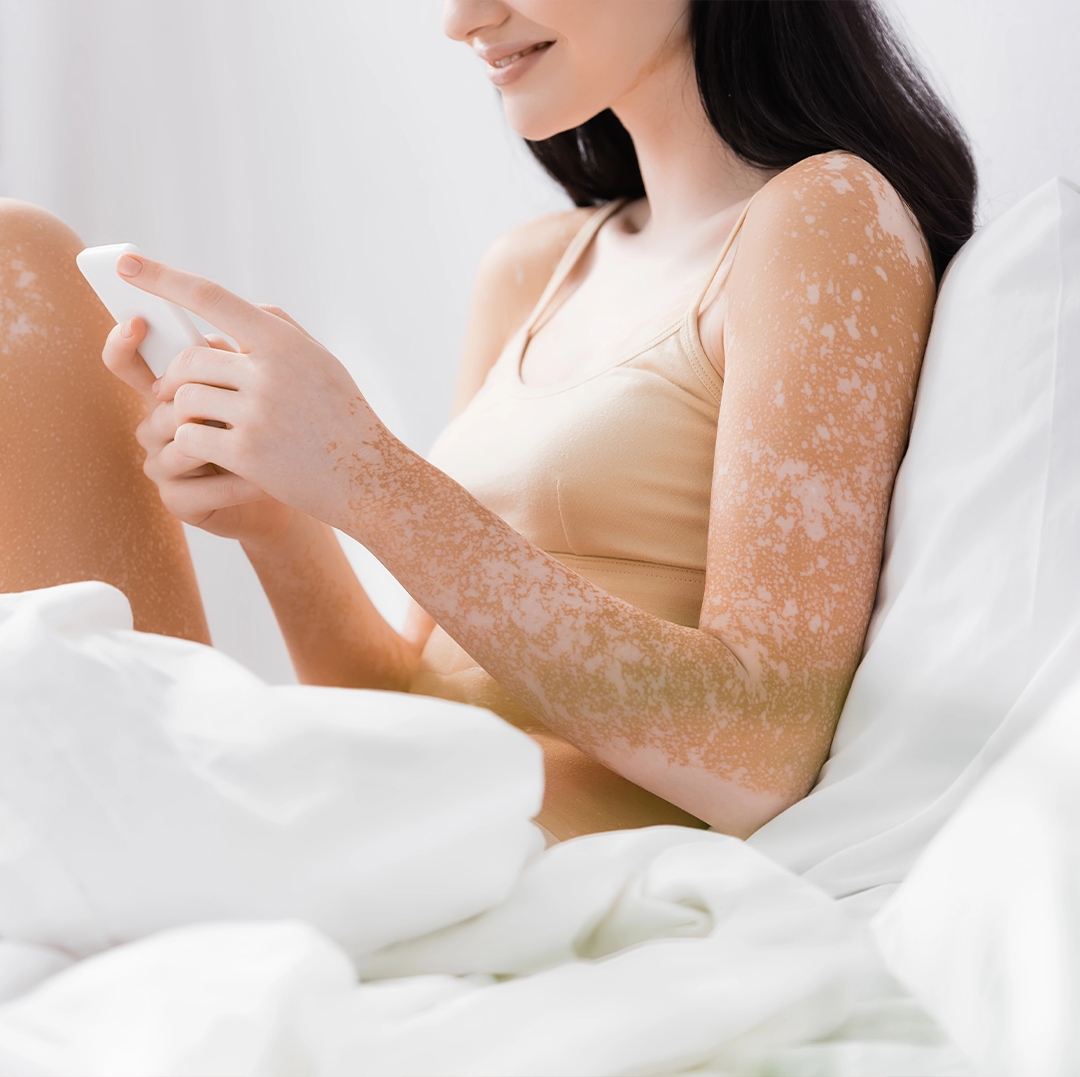
Vitiligo is a skin condition characterized by the loss of skin color, presenting as white patches that are often noticeable in society. Beyond its cosmetic appearance, it can also affect individuals psychologically and socially. Although the exact cause is not fully understood, the immune system, genetic factors, and environmental triggers are believed to play a role in its development.
While there is no definitive cure for vitiligo today, there are many methods aimed at restoring pigmentation and slowing disease progression. In this article, we will examine the current treatment options, patient experiences, and frequently asked questions with the precision of a dermatologist.
Understanding Vitiligo: Why Is It Important?
Vitiligo develops when melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, is no longer produced or when melanocytes are lost. The disease may remain limited to a few small spots or spread across the entire body. It is especially visible on sun-exposed areas such as the face, hands, elbows, and knees.
Its course varies from person to person. In some, it may remain stable for years, while in others it may progress rapidly. Therefore, treatment must always be personalized.
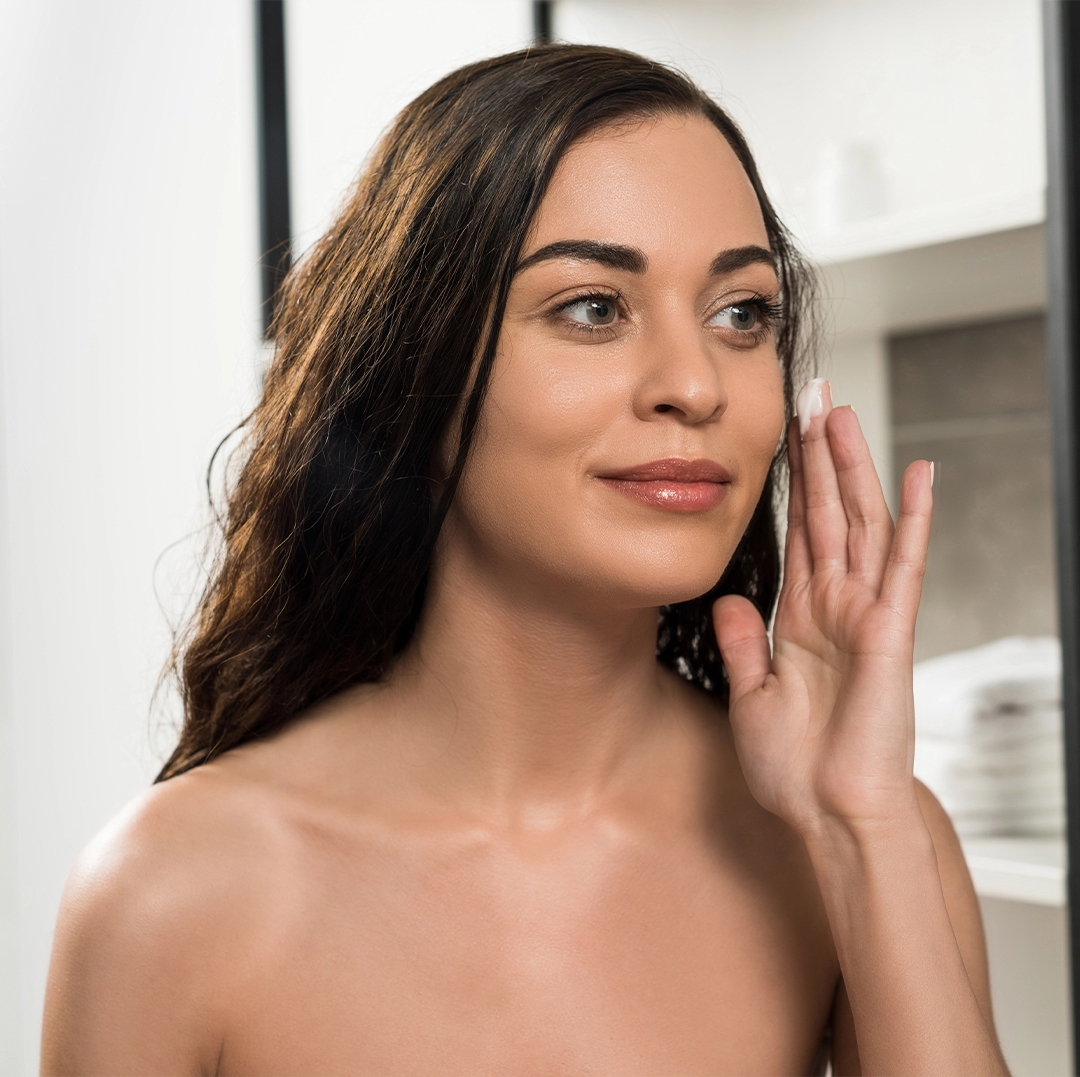
Topical Treatments
One of the first-line options for vitiligo involves creams and ointments applied directly to the skin:
Corticosteroid creams: Especially effective in new lesions. They may help repigment the skin but must be used under medical supervision due to possible side effects like skin thinning.
Calcineurin inhibitors (Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus): Steroid-free alternatives, safer for sensitive areas like the face, and often used in children.
Vitamin D analogs: Sometimes used alone or in combination with other topical therapies.
Topical treatments are generally preferred in early-stage or limited vitiligo cases.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
One of the most effective and reliable treatments for vitiligo is narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy.
Administered 2–3 times per week, with treatment lasting several months.
Most effective for newly developed, stable lesions.
Safe for both children and adults.
For smaller areas, excimer laser therapy can also be used, offering targeted light for faster results on localized patches.
Systemic Treatments
If vitiligo is rapidly progressing or covers large areas, systemic therapies may be considered:
Short-term oral corticosteroids: Used to slow disease activity.
Immunomodulatory drugs: Beneficial in selected cases.
New-generation therapies: JAK inhibitors (such as ruxolitinib) are under active research, targeting immune mechanisms involved in vitiligo and showing promising results.
Surgical Methods and Cell Transplantation
In patients who do not respond to conventional treatments and have stable vitiligo for a long time, surgical options may be considered:
Melanocyte transplantation: Involves transferring pigment cells from healthy skin to depigmented areas.
Epidermal grafting: Effective for small, localized patches.
These procedures should only be performed in specialized centers with proper patient selection.
Supportive Methods and Lifestyle Recommendations
Vitiligo may not always be completely treated, but quality of life can be improved with additional measures:
Sun protection: Vitiligo patches are more sensitive and should always be protected with high-SPF sunscreens.
Camouflage products: Cosmetic cover-up products can boost self-confidence.
Psychological support: Because vitiligo affects visible areas, it may impact self-esteem and social life; psychological support can be a valuable part of care.
Looking Ahead: Future Research
Research on vitiligo is expanding rapidly: Clinical trials with JAK inhibitors have shown repigmentation in many patients.
Stem cell research holds potential for more permanent solutions.
Molecular and genetic approaches may shape the future of vitiligo management.
Although not yet part of standard practice, these developments bring hope for patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can vitiligo be completely cured?
No, there is no permanent cure, but effective treatments can control the condition and significantly improve pigmentation.
Is vitiligo contagious?
No, vitiligo is not contagious. It is related to the immune system.
Does sun exposure make vitiligo worse?
Yes, unprotected sun exposure can trigger new spots or darken existing ones. Sunscreen use is essential.
Can children be treated for vitiligo?
Yes. Especially phototherapy and topical treatments can be safely used under dermatologist supervision.
Is psychological support necessary?
Yes. Because of its visible effects, vitiligo can cause self-esteem issues, anxiety, or depression. Psychological support complements medical treatment.
Vitiligo is a condition without a definitive cure but one that can be effectively managed. From topical creams and light therapy to surgical options and new-generation drugs, many treatments are available. The key lies in individualized planning, regular dermatologist follow-up, and patience—ensuring the best possible outcomes for each patient.

Editör
View All Articles