Why does skin dryness increase during winter? This is one of the most frequently asked questions in dermatology clinics as cold weather begins to set in. Low humidity, cold winds, dry indoor air from heating systems, and reduced water intake all contribute to the weakening of the skin barrier and increased moisture loss. As a result, the skin—both on the face and body—often becomes tight, flaky, cracked, and itchy.
What Is Skin Dryness?
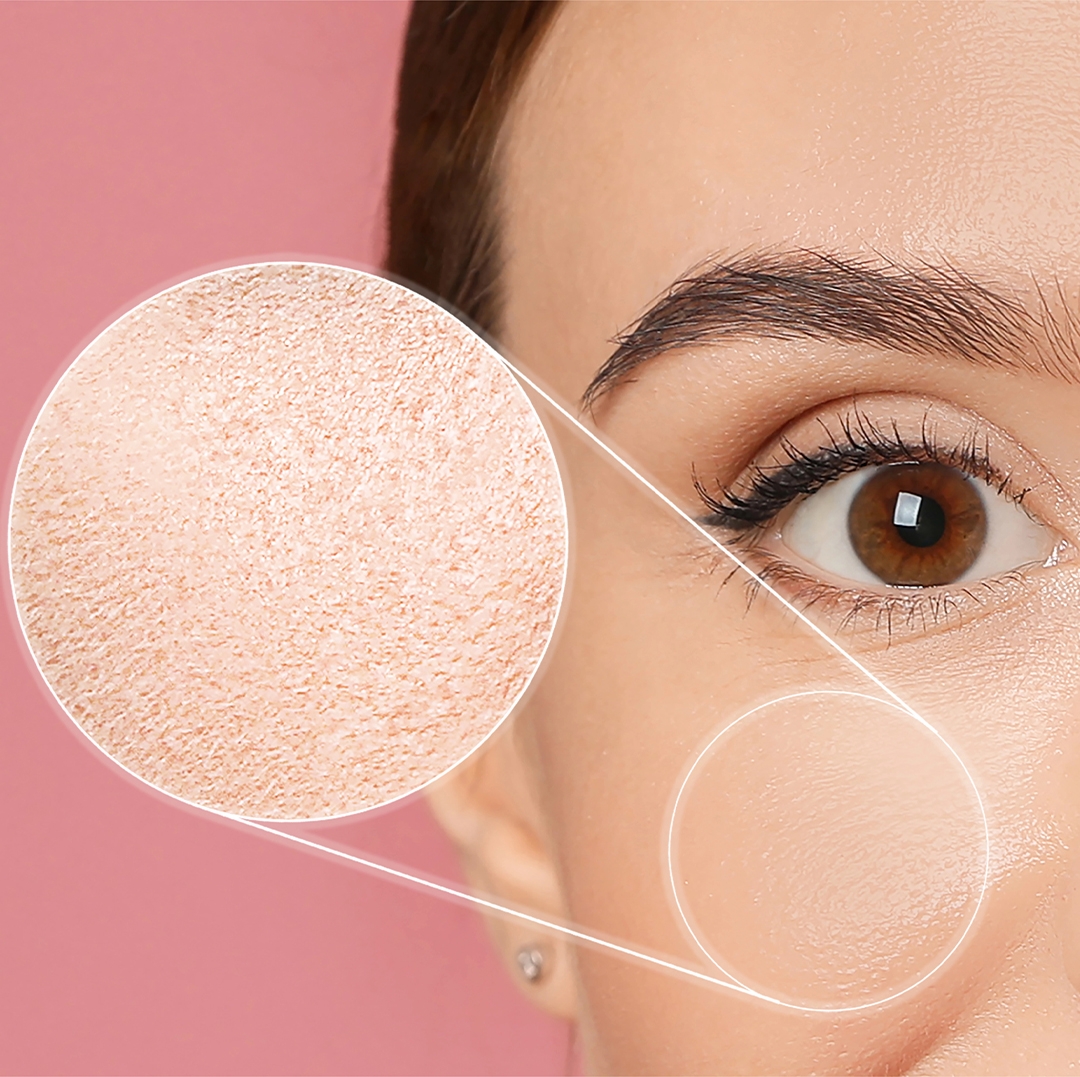
Skin dryness (xerosis) occurs when the balance of water and oils in the outer layer of the skin is disrupted. Normally, the skin stays soft and healthy thanks to a protective lipid layer and natural moisturizing factors (NMF) that lock in hydration. When this balance is disturbed, transepidermal water loss increases, the skin barrier weakens, and dryness develops.
Why Does Skin Dryness Worsen in Winter?
During the winter months, both environmental and behavioral factors negatively affect the skin’s moisture balance.
1. Low Humidity and Cold Air
The humidity level in the air drops significantly in winter. Cold air thins the natural lipid layer on the skin’s surface, accelerating water loss. Wind exposure further increases evaporation, leading to tightness and discomfort.
2. Dry Indoor Air
Heating systems such as radiators, stoves, and air conditioners reduce indoor humidity. Prolonged exposure to this dry air, especially overnight, can leave the skin tight and flaky by morning.
3. Reduced Water Intake
People tend to drink less water in cold weather due to a decreased sense of thirst. However, when the body’s fluid balance is disrupted, the skin is directly affected. Insufficient water intake slows down cell renewal and intensifies the feeling of dryness.
4. Hot Shower Habits
Long, hot showers may feel comforting during winter, but they strip the skin of its natural oils. This damages the skin barrier and increases water loss. Using harsh soaps or high-detergent cleansers further aggravates dryness.
5. Inadequate Moisturizer Use
Many people associate moisturizer use with summer. In reality, hydration products are even more important in winter. Moisturizers containing hyaluronic acid, ceramides, glycerin, or squalane help restore and strengthen the skin barrier.
Which Vitamin Deficiencies Cause Dry Skin?
Winter-related skin dryness can also result from vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Specifically, deficiencies in vitamins A, E, D, and B7 (biotin) can lead to moisture loss, dullness, and flakiness.
Vitamin A: Supports cell renewal; deficiency causes rough, uneven texture.
Vitamin E: An antioxidant that protects the lipid barrier.
Vitamin D: Production decreases during winter due to reduced sunlight, weakening the barrier.
Biotin (B7): Involved in keratin production; deficiency may cause cracks and irritation.
Can Skin Dryness Be a Sign of an Underlying Disease?
Not all dryness is caused by environmental factors. Persistent, itchy, or scaly dryness may signal underlying health issues such as:
Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Psoriasis
Diabetes
Hypothyroidism
Chronic kidney disease
In such cases, topical care alone is insufficient—medical treatment may be required. Therefore, persistent skin dryness should always be evaluated by a dermatologist.
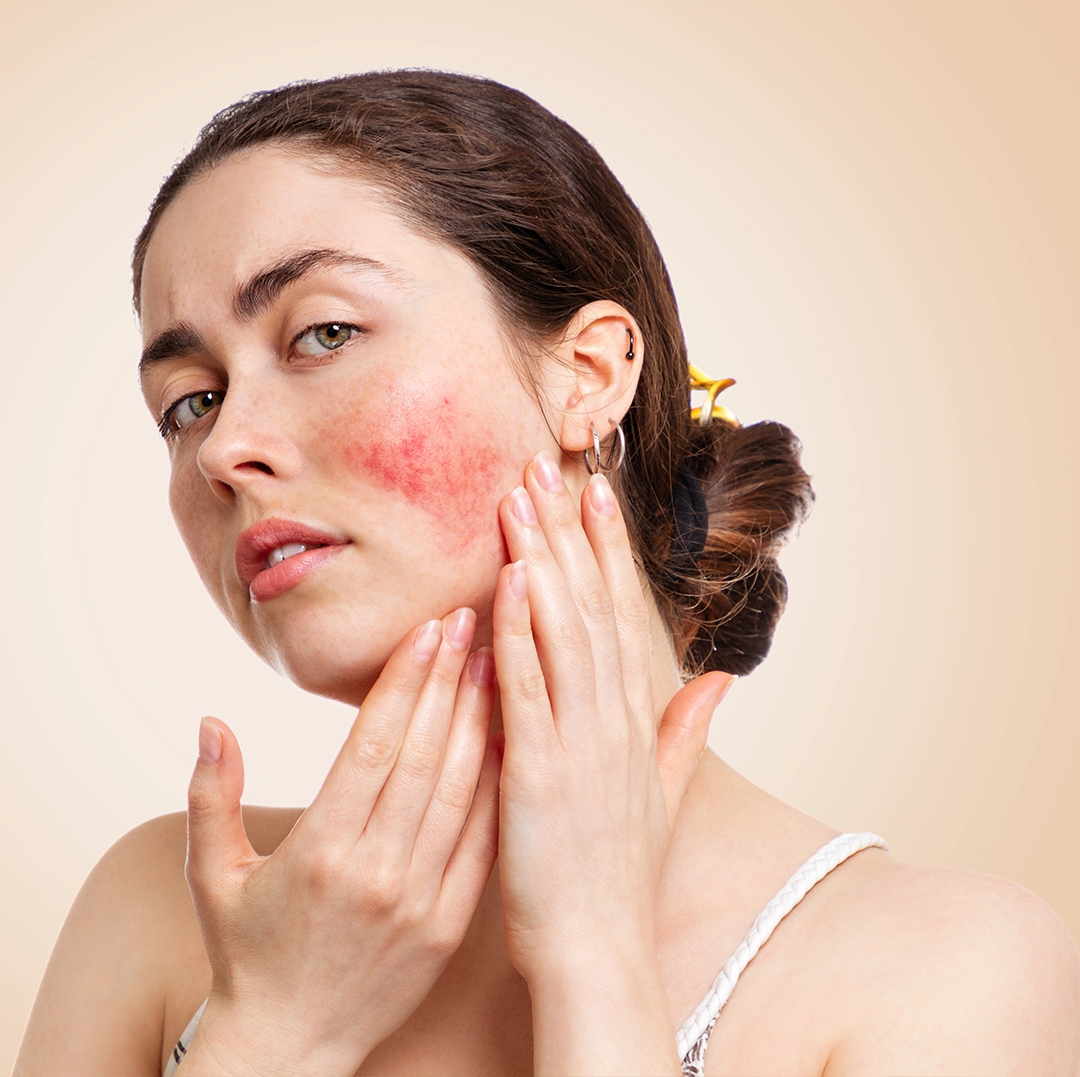
Why Does Facial Skin Dry Out More Easily?
The facial skin barrier is thinner and more exposed to external factors. Cold air, harsh wind, over-cleansing, and incorrect cosmetic use can deplete its protective oils. Additionally, matte foundations or alcohol-based toners used during winter can worsen dryness and irritation.
Symptoms of Skin Dryness
Dry skin manifests not only as a lack of moisture but also through several visible and sensory signs:
Tightness and sensitivity
Flaking and scaling
Itching, redness, and sometimes cracking
Noticeable dryness on the legs, elbows, hands, and face
These symptoms indicate that the skin’s moisture retention and barrier function are compromised.
How to Relieve Skin Dryness
The most effective way to prevent and reduce winter dryness is to establish a consistent skincare routine focused on barrier protection and hydration.
Use Lukewarm Water: Keep showers under 10 minutes and avoid overly hot water.
Choose Gentle Cleansers: Use pH-balanced, sulfate-free products instead of harsh soaps.
Moisturize After Showering: Apply moisturizer within 2–3 minutes after bathing while the skin is still slightly damp to lock in moisture.
Humidify Indoor Air: Use a humidifier or place a bowl of water in your room to increase air moisture.
Support with Vitamins: If necessary, consult your doctor about vitamin supplementation.
Stay Hydrated: Drink at least 1.5–2 liters of water daily to support skin cell hydration.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why does the skin become drier in winter?
Cold air, low humidity, and dry indoor environments cause moisture to evaporate from the skin. Hot showers and inadequate moisturization further worsen this effect.
2. Which vitamin deficiencies cause dry skin?
Deficiencies in vitamins A, E, D, and biotin (B7) can lead to dryness by impairing skin renewal and barrier function.
3. Can skin dryness indicate a medical condition?
Yes. Conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, diabetes, and thyroid disorders can cause chronic dryness. Persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
4. How can facial dryness be treated?
Avoid over-cleansing and alcohol-based toners, and use moisturizers with hyaluronic acid or ceramides to maintain hydration.
5. What should I do if dryness comes with itching?
Itching often indicates a damaged barrier. Along with moisturizing, use dermatologist-recommended barrier-repair creams or mild topical treatments as needed.

Editör
View All Articles