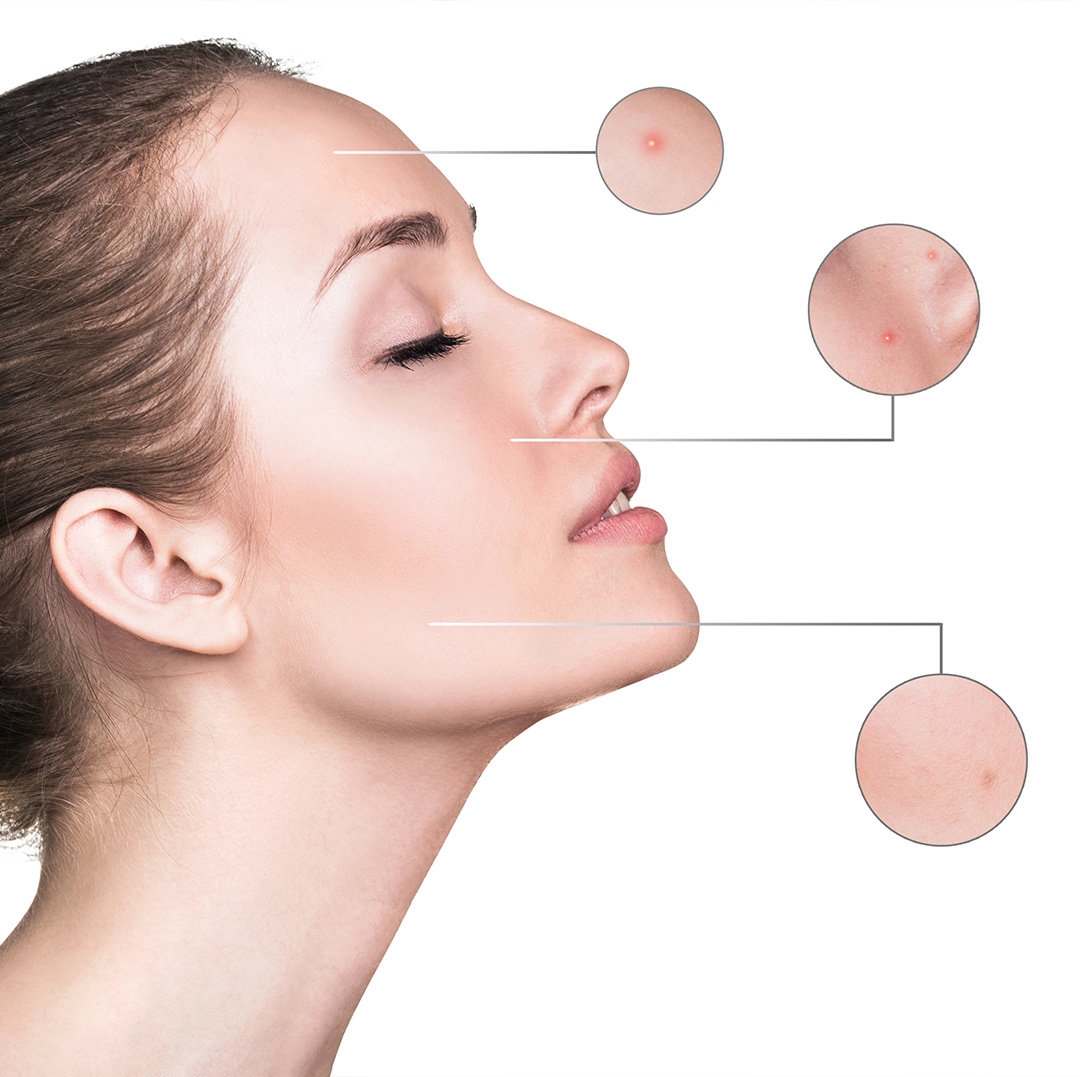
What skin symptoms indicate vitamin deficiencies? Many people visit dermatology clinics with complaints such as dullness, dryness, irritation, delayed healing, or overall loss of radiance. While these symptoms often stem from environmental factors, improper skincare habits, or a weakened skin barrier, in some cases vitamin deficiencies can also play a noticeable role in skin changes.
In this article, I explain the role of vitamins in skin biology, which deficiencies manifest through which symptoms, how to recognize these signs, and why these deficiencies matter from a dermatological perspective—strictly for informational purposes.
Why Are Vitamins So Important for Skin Health?
The skin is the largest organ of the body, and vitamins are essential for its proper function.
Key roles of vitamins in skin health include:
- Supporting cell renewal
- Providing antioxidant protection
- Contributing to collagen synthesis
- Maintaining barrier integrity
- Regulating pigmentation processes
- Helping manage inflammation
When these vitamins decrease, the skin often reflects the change quickly.
Which Vitamin Deficiencies Affect the Skin?
Below are the most commonly observed vitamin deficiencies and the skin-related signs associated with each.
1. Vitamin A Deficiency: Dryness, Rough Texture, and Delayed Healing
Vitamin A plays a major role in keratinization, collagen synthesis, and the cell renewal cycle.
Deficiency may lead to:
- Dry, rough skin
- Flaking
- Increased irritation
- Dull appearance
- Follicular keratosis (“chicken skin”)
- Delayed healing of skin injuries
Vitamin A deficiency is more common in individuals with restricted diets or malabsorption issues.
2. B Vitamins (B7 and B12): Dullness, Dryness, and Pigmentation Changes
B vitamins support the skin barrier and energy metabolism.
B7 (Biotin) deficiency may cause:
- Dry, thin skin
- Flaking
- Rash-like symptoms around the face or arms
- B12 deficiency may cause:
- Noticeable paleness
- Tired, dull skin tone
- Hyperpigmentation in some cases
B12 deficiency is especially common among individuals with vegan diets or absorption disorders.
3. Vitamin C Deficiency: Reduced Collagen and Easy Bruising
Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant and critical for collagen production.
Deficiency may result in:
- Decreased elasticity
- Easy bruising
- Slower wound healing
- Dull, tired appearance
- Dryness
Severe deficiency (scurvy) is rare today but milder forms are still seen.
4. Vitamin D Deficiency: Dryness, Redness, and Barrier Weakness
Vitamin D has an important role in immune regulation and skin barrier function.
- Deficiency may cause:
- Dryness
- Redness or inflammation
- Atopic dermatitis–like symptoms
- Increased barrier vulnerability
Vitamin D deficiency is especially common in individuals with limited sun exposure.
5. Vitamin E Deficiency: Increased Sensitivity and Oxidative Stress
Vitamin E is a key antioxidant that protects the skin’s lipid barrier from oxidative damage.
- Deficiency may cause:
- Increased sensitivity
- Redness
- Dryness and irritation
- Dull surface appearance
Lower tolerance to environmental stressors (wind, cold, pollution)
6. Vitamin K Deficiency: Easy Bruising and Dark Under-Eyes
Vitamin K contributes to blood clotting mechanisms.
Deficiency can lead to:
- Easy bruising
- More pronounced dark under-eye circles
- Increased visibility of superficial veins
Why Do Vitamin Deficiencies Show Up on the Skin So Quickly?
Because the skin responds rapidly to metabolic changes.
Reasons the skin is sensitive to vitamin levels include:
- Rapid cell turnover
- Rich microvascular structure
- Dependence on vitamins for barrier health
- Requirement of vitamins for collagen synthesis
Thus, decreasing vitamin levels often show up first in the skin.
How Does Vitamin Deficiency Skin Typically Look?
In general, skin affected by vitamin deficiency may appear:
- Pale
- Dull
- Dry
- Easily irritated
- Slow to repair
- More fragile
Some individuals may develop fine cracks, redness episodes, or rash-like patterns.
Which Skin Types Show Vitamin Deficiency Signs More Clearly?
Dry and Sensitive Skin
Shows symptoms more rapidly.
Atopic Skin
Has weaker baseline barrier function, making deficiencies more noticeable.
Oily Skin
Often shows fewer symptoms but B12 deficiency may still affect pigmentation.
Aging Skin
Reduced collagen production makes deficiency effects more visible.
Understanding the Biological Link Between Vitamins and the Skin
Vitamin deficiencies affect the skin through four key mechanisms:
Slowed Cell Renewal
Keratinocyte turnover decreases, leading to dullness.
Reduced Collagen Production
Especially notable in vitamin A and C deficiency.
Weak Antioxidant Defense
Vitamin C and E deficiencies increase oxidative stress.
Impaired Barrier Function
Weak barrier integrity leads to dryness and irritation.
Do Skin Symptoms Always Indicate a Vitamin Deficiency?
No. Similar symptoms can appear due to:
- Eczema
- Contact dermatitis
- Over-exfoliation
- Incorrect product use
- Cold weather
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Poor sleep
A vitamin deficiency should be confirmed by an authorized healthcare professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can a vitamin deficiency be recognized on the skin?
Dryness, dullness, delayed healing, and some pigmentation changes may indicate deficiency.
Which vitamin deficiencies affect the skin the most?
A, B12, C, D, E, and K deficiencies can all produce noticeable skin symptoms.
Can vitamin deficiency cause hyperpigmentation?
Yes. B12 deficiency in particular may contribute to pigmentation changes.
Does dryness mean vitamin deficiency?
Not always, but deficiencies in A, C, D, and E vitamins can contribute to dryness.
Does vitamin deficiency accelerate skin aging?
Indirectly, yes—reduced collagen and antioxidant protection can contribute to early aging signs.

Editör
View All Articles